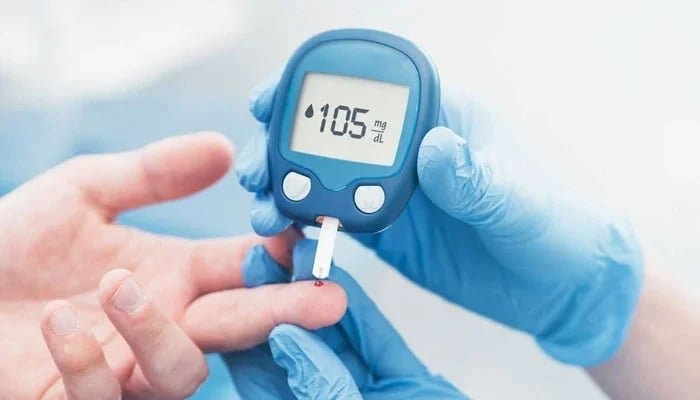
Diabetes is a chronic and serious condition that affects one in every ten individuals, with the number of cases steadily increasing. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form, accounting for 90 to 95 percent of cases, while Type 1 diabetes and gestational diabetes are also significant variants.
All forms of diabetes share a common characteristic: an increase in the level of sugar in the blood, referred to as blood sugar. Our bodies produce insulin to control blood sugar levels.
Insulin, a hormone produced in the pancreas, facilitates the entry of glucose into cells, where it is converted into energy. When we eat, food is converted into glucose, triggering the release of insulin from the pancreas, which opens the gates of cells to allow glucose to enter and be converted into energy.
Consistently elevated blood sugar levels increase the risk of Type 2 diabetes. However, it’s not just sugary foods or beverages that can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels; several other surprising factors can also increase this risk.
Factors such as heart attacks and heart diseases can be avoided by engaging in how much exercise? The body’s response to stress and fear plays a significant role in increasing blood sugar levels. When our bodies sense a threat, a mechanism called fight-or-flight is activated, during which glucose is released into the blood to provide energy for confrontation or escape.
This results in an increase in blood sugar levels, and the risk of Type 2 diabetes rises with chronic stress. Sleep deprivation affects hormonal balance, leading to increased insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels.
A lack of sleep also increases the desire for sweet foods, further raising blood sugar levels. Excessive salt consumption While it is generally believed that consuming too much sugar increases the risk of diseases like diabetes, excessive intake of salty foods can also lead to this deadly disease.
Research conducted at Tulane University in 2023 revealed that individuals who regularly sprinkle salt on their food are at an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Similarly, each additional use of salt raises the risk of diabetes diagnosis by up to 39 percent. Artificial sweeteners Artificial sweeteners can also increase blood sugar levels. Generally used as an alternative to sugar, artificial sweeteners can have negative effects on insulin levels and sensitivity, contributing to elevated blood sugar levels.
Fiber deficiency A deficiency of fiber in the diet can also make one prone to high blood sugar. Fiber is a dietary component that slows down the absorption of sugar into the blood, stabilizing blood sugar levels.
A lack of fiber in the diet and a high intake of refined carbohydrates lead to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels after eating. Aging Aging is also associated with a decrease in the body’s ability to control blood sugar levels.
This is why the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes increases after the age of 40. However, despite aging, maintaining healthy habits such as exercise and a balanced diet can stabilize blood sugar levels. Note: This article is based on information published in medical journals; readers should also consult their healthcare provider for advice.