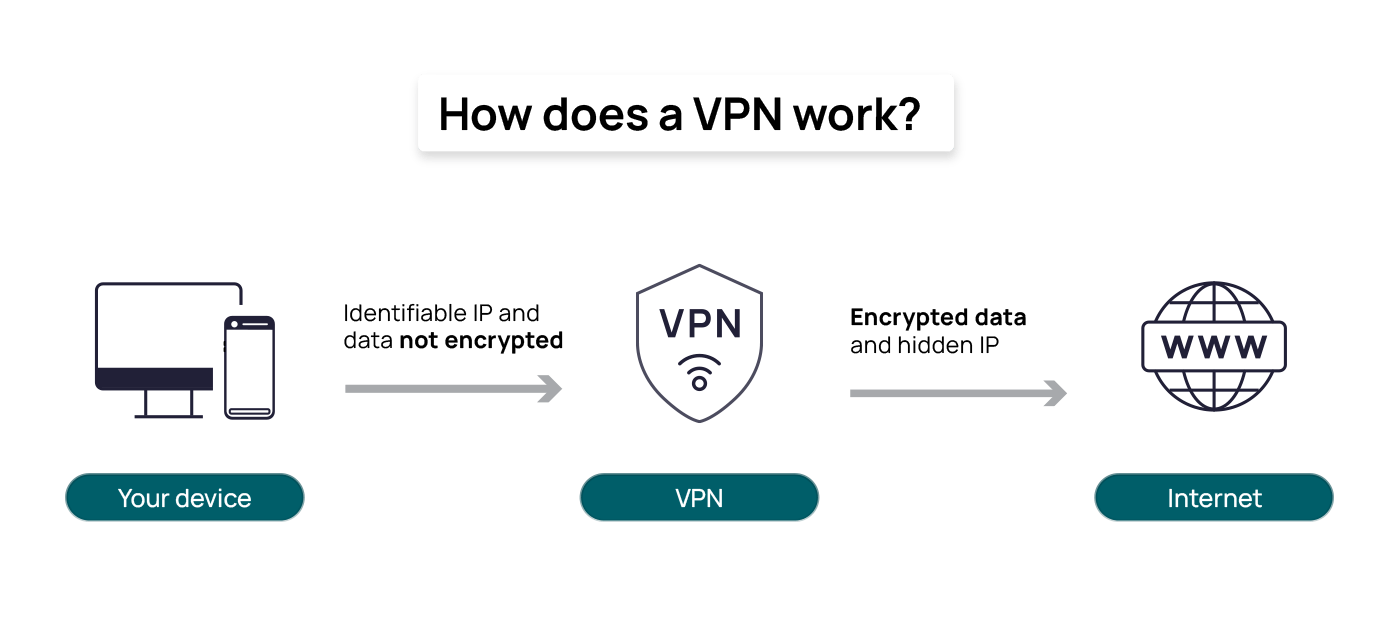
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a service that encrypts your online activity and routes it through secure servers, effectively hiding your data from anyone trying to access it. This is akin to riding in a limo with tinted windows, providing privacy and security compared to the more exposed city bus of regular internet use.
Why Use a VPN?
- Privacy Protection: Prevents electronic eavesdropping on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Location Spoofing: Allows you to appear as if you’re browsing from a different location, which can help access localized content or bypass censorship.
- Home Use: Can hide your activities from your internet service provider, although it’s less necessary if your network is secure and password-protected.
VPN Legality
- Legal in Most Countries: VPNs are generally legal worldwide, but there are exceptions in countries with strict internet controls, like China and North Korea.
Choosing a VPN
- Research and Reviews: Look for tech review sites that evaluate VPNs based on privacy, encryption, speed, and ease of use.
- Reputable Providers: Consider well-known services like NordVPN, Mullvad, ProtonVPN, Surfshark, ExpressVPN, and Private Internet Access.
- Key Features:
- Kill Switch: Ensures your data remains secure if the VPN connection drops.
- No-Logging Guarantee: Ensures no recording of your online activities; look for third-party audits to confirm compliance.
- Paid Services: Typically offer better security and performance compared to free VPNs.
Risks of Free VPNs
- Sub-Par Security: Many free VPNs lack robust security measures.
- Data Harvesting: Some may collect and sell your data.
- Performance Issues: Free VPNs often have too many users on limited servers, leading to slower speeds.
- Potential Malware: Some free VPNs can contain malware or inject ads into your browsing experience.
Installation and Setup
- User-Friendly: Most VPNs are easy to install and configure on computers, smartphones, or browsers.
- Protocol Choices: Common protocols include WireGuard for speed and OpenVPN for strong encryption, both considered safe.
Downsides of VPNs
- Reduced Speed: VPNs can slow your internet by 5-10% due to the encryption process.
- Increased Captchas: You might encounter more verification puzzles or be blocked by certain websites.
- Streaming Restrictions: Some services, like DAZN and BBC iPlayer, actively block VPN traffic.
Using a VPN is a prudent step towards ensuring your online privacy and security, especially on public networks. While there are minor drawbacks, the benefits of safeguarding your personal information and accessing content securely often outweigh the inconveniences.